Sexually Transmitted Diseases
STDs, or sexually transmitted infections (STIs), refer to infections that are primarily transmitted via sexual contact — vaginal, oral or anal intercourse. STDs can happen to anyone who is sexually active, but can also be effectively cured with the right treatment.
The first step to treating STDs starts with determining what type of STD you have through proper screening.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
HIV is a type of STD spread primarily through unprotected sexual contact. The virus is found primarily in bodily fluid, making sexual intercourse the most common way it spreads. HIV can also be transmitted through:
- Sharing used syringes or needles
- Unregulated and unscreened blood transfusions
- From mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth or breastfeeding
HIV, if left untreated, can lead to a serious and life-threatening condition known as Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS).
STD/ HIV Screening Packages in Singapore
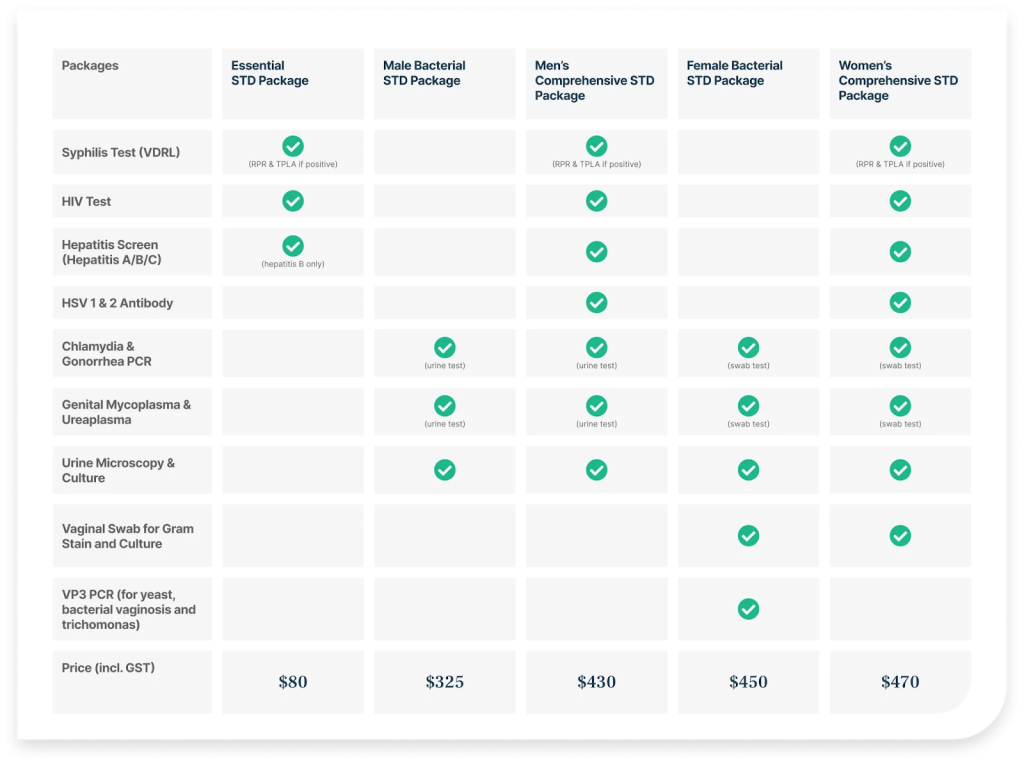
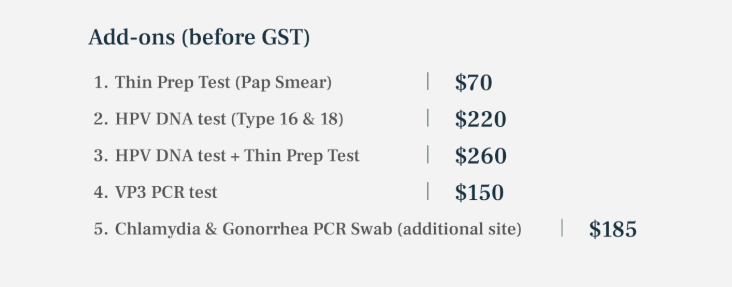
What are the common types of STDs and HIV?
Common STDs include:
- Chlamydia – Chlamydia is an STD caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis, it is also the most common curable STD.
- Gonorrhea – Gonorrhea is caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and is considered the second most common STD worldwide [1, 2].
- Syphilis – Syphilis is caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum. The bacteria is slow-growing, screening and testing using culture tests or light microscopy is difficult, hence venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) test is done to screen for syphilis infections.
- Trichomonas – Trichomonas infections are caused by a single-celled protozoa called Trichomonas vaginalis. The infections caused ulcers in the vagina, cervix, urethra, and paraurethral glands.
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV) – HSV infections are caused by HSV-1 and HSV-2 viruses. HSV-1 is commonly associated with cold sores around the mouth, while HSV-2 infections are associated with genital herpes. HSV infections are lifelong and can recur throughout your life [3].
- HIV – HIV is a type of STI that is responsible for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) [4]. The virus targets the CD4+ T cells in our immune system, suppressing and killing the cells, hence leading to a weakened immune system. HIV can be treated with antiviral medications to suppress viral activity.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) – Infections of HPV are known to cause warts. There are more than 100 types of HPV, which can be further classified as high-risk types and low-risk types. High-risk types 16 and 18 are associated with malignancy and cervical cancer [1].
- Hepatitis virus (HAV, HBV, HCV) – Hepatitis viruses are not all considered STDs, but HBV and HCV can be spread via sexual contact. Hepatitis infections target the liver and cause symptoms such as jaundice, dark fever, fatigue, dark urine, and pale or clay-coloured stool.
Why do I need to screen for STD/HIV?
Screening and detection of STDs and HIV helps protect both yourself and public health. Many sexually transmitted infections are asymptomatic, which means you may carry and spread the infection without knowing it.
Early detection and screening also allows you to receive treatment before the disease progresses and causes other complications, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), infertility, or the progression of infections like HIV.
When should I get tested for STD/HIV?
Ideally, testing and screening should be done regularly or routinely if you:
- Are sexually active
- Have multiple sexual partners
- Had casual unprotected sex
- Have a history of STIs or STDs
- Was forced to engage in sexual activity
- Share needles
- Are pregnant
Signs and symptoms of STD/HIV infection
If you suspect an STD, it is highly recommended to perform an STD/HIV screen for a diagnosis in order to receive the proper treatment. Common signs and symptoms of STDs are as follows:
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) symptoms
| In Women |
| Vaginal itching or painBurning sensation during urinationAbnormal, foul-smelling dischargeVaginal pain during sexVaginal bleeding outside of periodsWarts, ulcers or sores around the mouth, genitals or anusLower abdominal painFever Swollen lymph nodes |
| In Men |
| Painful urinationBurning or itching around the opening of the penisDischarge from the penisPain during sexPain or swelling of the testiclesBlisters or sores around the mouth, genital or anusFever Swollen lymph nodes |
Symptoms of STDs may vary depending on the type of infection you have. Some infections may also be asymptomatic.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) symptoms
| Acute HIV |
| Most cases of acute HIV present symptoms within 4 weeks after infection with HIV. FeverFatigueMuscle painSkin rashHeadacheSore throatDiarrhoeaSwollen lymph nodesJoint painUlcers in the mucosal membranes of the mouth or genitals Some of these early symptoms are non-specific and can often be confused with other illnesses. |
| Chronic HIV |
| When acute HIV is not treated, the virus can further replicate, leading to chronic HIV. Most patients with HIV can also be asymptomatic until it progresses into AIDS [4]. FatigueSwollen lymph nodesCandidiasis, which can be oral or vulvovaginalDiarrhoeaWeight lossFever Shortness of breath |
AIDS
Chronic HIV, when left untreated, can result in AIDS, a condition characterised by a severely weakened immune system. Among the AIDS-defining conditions outlined by the CDC include [4]:
- Candidiasis (digestive and pulmonary tract)
- Invasive cervical cancer
- Meningitis
- Tuberculosis
- HIV encephalitis or other HIV-associated neurological infections
- Lymphoma
- Mycobacterial infections
- Pneumonia
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
Types of STD Tests
Tests for STDs and HIV are performed based on the type of infectious agent.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) – PCR involves detection of the genetic materials of the pathogen, such as DNA or RNA. Samples can be taken from blood, or from swabs from your mouth, or genital area.
- Antibody tests – Antibodies are a type of protein produced by your immune system to fight off the pathogen. Presence of an antibody against a specific pathogen in your body may indicate that you have had an exposure to said pathogen. Antibody tests are commonly used in hepatitis screening. Another common type of antibody test is te VDRL test for syphilis.
- Antigen tests – Antigens are proteins which can be on the surface or inside of a bacteria or virus. Antigen tests can be done to detect the presence of the bacteria or virus.
- Thin prep test (Pap smear) – Thin prep tests are commonly done to observe cytological features of the cells, this means that your doctor will scrape off samples of cells from the cervix using a brush-like device. They will then observe the cells for changes in shape or form that may indicate inflammation or malignancy of the cells.
- Culture tests – Culture tests are done to identify bacterial or fungal species that may cause disease and infection. Samples are typically taken from genital mucous membranes or the urine, the samples are then added to a nutrient-rich medium, such as an agar or a broth. If bacteria is present, the bacteria will grow in this medium and can be further analysed and identified.
What to expect during a STD/HIV Test?
Generally, STD/HIV tests are quite straightforward and can be done by your doctor in-clinic. Tests recommended will depend on your symptoms and the specific types of infection you intend to screen for.
Consultation
Before any tests, a consultation with our doctor is done to understand your sexual history, symptoms, and potential exposure to determine what types of STDs to test for.
Sample collection
- Blood sample — Blood samples may be taken to test for STDs such as HIV or syphilis.
- Urine samples — Urine samples help test for the presence of chlamydia or hepatitis.
- Swabs — Swabs taken from the genital area, throat, or rectum may be taken.
Results
Depending on the type of tests, results can be ready within a day or two. Once you receive your results, you may be asked to come back for a follow-up consultation session, medical treatment, or for referral to a specialist.
For further inquiries on STD and HIV testing, please do not hesitate to reach out to us.
Are my STD results kept confidential?
Rest assured, your STD results are kept strictly confidential. In Singapore, patient confidentiality is protected by law and your results will not be shared with your employers, family members or partners without your explicit consent.
Frequently Asked Questions
When should I go for a STD/HIV test?
Sexually active individuals are highly encouraged to go for routine or regular screens and check-ups. It is recommended to screen for STDs/HIV when you:
- Have a new sexual partner
- Have multiple sexual partners
- Have had unprotected sex
- Are pregnant (as a means to prevent vertical transmission)
In other cases, you should go for an STD screen if you experience symptoms of an STD/STI.
Can HIV be cured?
There is no cure for HIV as of now, however HIV can be treated and managed with antiviral medications. Practising safe sex and use of preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) are recommended for those at high risk of exposure to HIV infections.
References
- Garcia MR, Leslie SW, Wray AA. Sexually Transmitted Infections. 2024 Apr 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 32809643.
- Springer C, Salen P. Gonorrhea. 2023 Apr 17. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 32644329.
- Cole S. Herpes Simplex Virus: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Nurs Clin North Am. 2020 Sep;55(3):337-345. doi: 10.1016/j.cnur.2020.05.004. Epub 2020 Jul 15. PMID: 32762854.
- Swinkels HM, Justiz Vaillant AA, Nguyen AD, Gulick PG. HIV and AIDS. 2024 Jul 27. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30521281.

